| x2−2x+2 | ||
2)f(x)= | ||
| x−1 |
| x2 | 8 | |||
3)f(x)= | + | |||
| 2 | x2 |
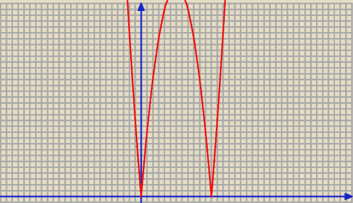 1) f(x) = |x(x−12)|2
Ekstrema finkcji g(x)=|x(x−12)| znamy (to wiedza o funkcji kwadratowej), a więc f ma ekstrema w
tych samych punktach co g i ekstrema te sa równe ...
1) f(x) = |x(x−12)|2
Ekstrema finkcji g(x)=|x(x−12)| znamy (to wiedza o funkcji kwadratowej), a więc f ma ekstrema w
tych samych punktach co g i ekstrema te sa równe ...
| x2−2x+1 + 1 | (x−1)2 + 1 | (x−1)2 | 1 | |||||
2) f(x) = | = | = | + | = x−1 + | ||||
| x−1 | x−1 | x−1 | x−1 |
| 1 | ||
| x−1 |
| 1 | t2+1 | t2−2t+1+2t | (t−1)2+2t | (t−1)2 | ||||||
f(t) = t + | = | = | = | = | + | |||||
| t | t | t | t | t |
| 2t | (t−1)2 | |||
= | + 2 zatem dla t=1 funkcja osiąga minimum | |||
| t | t |
| 1 | t2+1 | t2+2t+1−2t | (t+1)2 | |||||
f(t) = t + | = | = | = | − 2, więc dla t=−1 jest | ||||
| t | t | t | t |