| 1−cos x | ||
a) f(x)= | ||
| sin x |
| 1 | ||
Wyznaczyć ekstremum oraz przedziały monotoniczności funkcji określonej wzorem : y=x2 e | ||
| x |
| 1 | ||
( | to potęga e) | |
| x |
| 1 − cos x | ||
a) f(x) = | ; x ≠ k*π gdzie k jest liczbą całkowitą | |
| sin x |
| f | f '*g − f* g' | |||
( | ) ' = | |||
| g | g2 |
| sin x * sin x − ( 1 − cos x)*cos x | ||
f ' (x) = | = | |
| sin2 x |
| sin2 x − cos x + cos2 x | 1 − cos x | |||
= | = | |||
| sin2 x | sin2 x |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
= e ln √ x − 1 * | * | *1 = 0,5*eln √x −1* | = | |||
| √x−1 | 2 √x−1 | x −1 |
| 0,5 e ln √x −1 | ||
= | ||
| x − 1 |
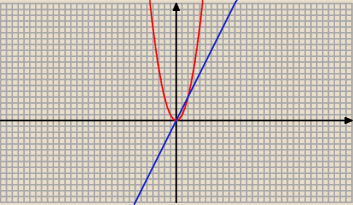 y = x2
y = 2 x
x2 = 2x
x2 −2x = 0
x*( x − 2) = 0
x1 = 0 x2 = 2
zatem pole
2 2 2 2
y = x2
y = 2 x
x2 = 2x
x2 −2x = 0
x*( x − 2) = 0
x1 = 0 x2 = 2
zatem pole
2 2 2 2
| 1 | ||
P = ∫ 2x dx − ∫ x2 dx = ∫ ( 2 x − x2 ) dx = [ x2 − | x3 ] = | |
| 3 |
| 1 | 8 | 4 | ||||
= 22 − | *23 = 4 − | = | ||||
| 3 | 3 | 3 |